Smart Green Houses: Solutions for Sustainable Living

INTRODUCTION:
Smart green houses are shining examples of the future of sustainability, thriving at the dynamic nexus of cutting-edge technology and environmentally responsible living. These homes skillfully use cutting-edge technologies, such as computerized climate management and renewable energy sources, to create a lifestyle that is in harmony with the environment and is energy-efficient. Come along for the ride as we explore the revolutionary world of smart green houses, where the necessity of ecological stewardship collides with the inventiveness of genius.
Definition of smart green houses:
Smart green houses can be defined as intelligently designed dwellings that harness the power of innovative technologies and eco-friendly principles to create sustainable, energy-efficient living spaces. These homes seamlessly integrate cutting-edge features such as automated climate control, renewable energy sources, intelligent lighting systems, and advanced waste reduction strategies. The essence of smart green houses lies in their ability to adapt to the evolving needs of both inhabitants and the environment, offering a harmonious blend of technological sophistication and environmental responsibility.
Key Features of Smart Green Houses:
Climate control that is automated:
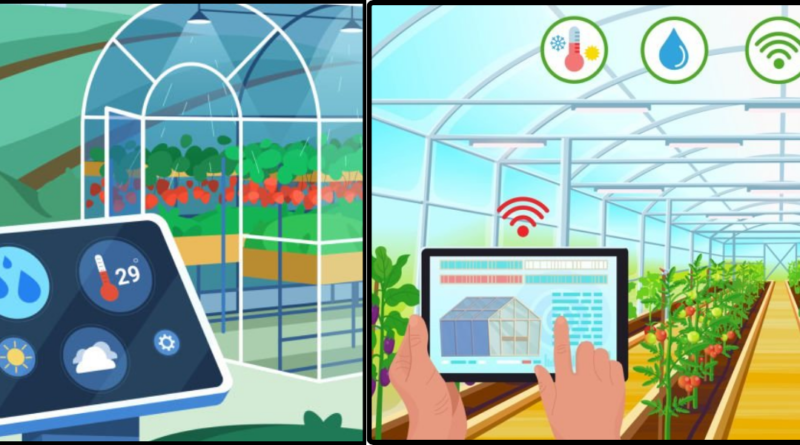
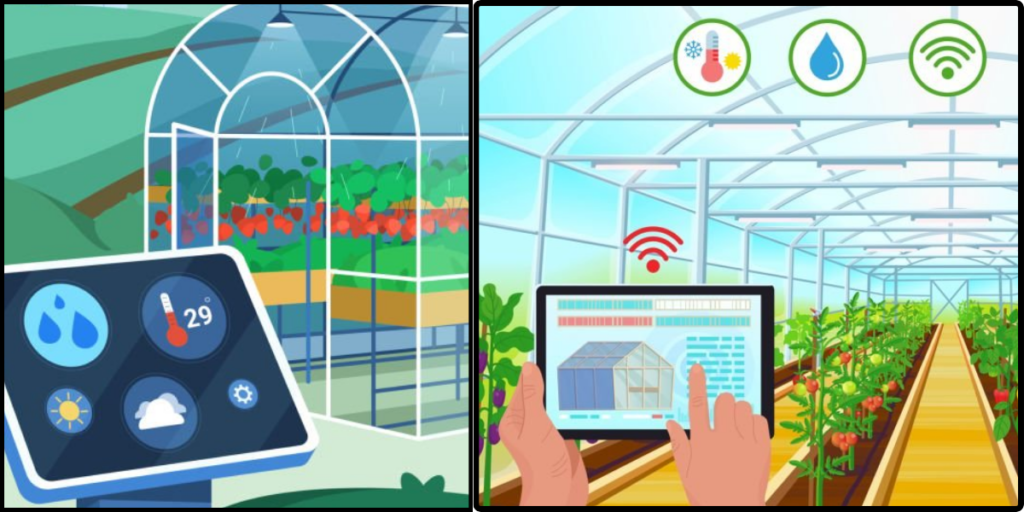
Intelligent temperature control systems, which optimize HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) based on real-time data, are a feature of smart green houses. In the process, you save energy consumption and guarantee a comfortable living space.
Integration of Renewable Energy:
To produce power, smart green houses frequently include solar panels, wind turbines, or other renewable energy sources. This helps to reduce carbon emissions and reduce dependency on conventional power networks.
Systems for managing water:
Sustainable development must prioritize water conservation. Water-saving techniques, including rainwater collection, water recycling, and intelligent irrigation systems, are used in smart green houses to maximise water usage.
Smart Lighting Options:
Residents may adjust illumination according to their tastes and the time of day with the help of automatic controls and energy-efficient LED lights. By doing this, energy waste is reduced and a more balanced circadian cycle is promoted.
Strategies for reducing waste:
Smart green houses work to reduce trash creation by putting in place composting solutions and waste separation systems. Trash disposal is optimized using smart bins with sensors, which notify inhabitants when the bins are full.
Advantages of Smart Green Houses:
The advantages of smart green houses are multifaceted, encompassing environmental, economic, and lifestyle benefits. Here are some advantages:
Energy Efficiency:
The cutting-edge technology used in the construction of smart green houses maximizes energy usage. Reduced energy usage results in cheaper utility bills and a lower environmental impact. Examples of these reductions include automated climate control, energy-efficient lighting systems, and the incorporation of renewable energy sources.
Cost Savings:
When renewable energy https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Renewable_energy sources are used in conjunction with energy-efficient measures, homeowners may save a considerable amount of money. Smart green houses are financially sustainable overall because they use less energy and water and have more efficient waste management systems.
Improved indoor air quality:
Smart green houses often incorporate advanced ventilation and air purification systems. This results in improved indoor air quality, creating a healthier living environment by reducing allergens, pollutants, and the risk of respiratory issues.
Environmental Conservation:
Smart green houses are vital to environmental preservation as they employ sustainable techniques and renewable energy sources. The worldwide effort to address climate change is aided by a decreased carbon footprint and a decreased reliance on non-renewable resources.
Customized Living Experience:
The integration of smart technologies allows residents to customize their living spaces according to their personal preferences. Automated lighting, climate control, and security systems offer a level of convenience and comfort that enhances the overall quality of life within the smart green house.
Technological Innovation:
Smart green houses are at the forefront of technological innovation. As these homes continue to evolve, they serve as living laboratories for emerging technologies, ensuring that residents benefit from the latest advancements in home automation and artificial intelligence Sustainable Agriculture through Robotics and Automation, and sustainable design.
Resilience and Future-Proofing:
Purchasing a smart green house makes one resilient to upcoming environmental issues and changes in regulations. For those who are devoted to long-term sustainability, these houses offer a forward-thinking and future-proof option because of their flexibility to adapt to new technology.
Reduced water consumption:
Intelligent water management solutions, such as effective irrigation and rainwater collection, are frequently included in smart green houses. This not only reduces water usage but also helps with water conservation, especially in areas where water is scarce.
Increased property value:
The growing demand for sustainable living has led to an increase in the value of properties equipped with smart green features. Homebuyers are increasingly prioritizing eco-friendly homes, making smart green houses not only environmentally responsible but also attractive investments.
Community and Global Impact:
Smart green practices are a way for households to get involved in the greater movement of sustainable living. Numerous smart green houses working together can foster environmentally conscious communities and have a significant impact on international efforts to combat resource depletion and climate change.
Smart Resource Management:
Smart green houses utilize sensors and automation to intelligently manage resources such as water, electricity, and heating. This ensures that resources are used efficiently, reducing waste and promoting sustainable consumption patterns.
Integration of Renewable Energy:
Utilizing sustainable energy sources like solar and wind turbines is one of the unique aspects. This lessens dependency on conventional energy networks and helps provide sustainable, clean energy.
Eco-Friendly Construction Materials:
Smart green houses are often constructed using eco-friendly and sustainable building materials. This not only reduces the environmental impact associated with construction but also ensures a healthier indoor environment for residents.
Tax Incentives and Rebates:
Many governments and municipalities offer tax incentives or rebates for homeowners who invest in energy-efficient and sustainable features. Smart green houses, therefore, not only contribute to personal savings but may also qualify for financial benefits from the authorities.
Adaptability to Urban Planning:
Smart, green homes may play a crucial role in sustainable urban design Sustainable Tech Innovations in Urban Farming: Cultivating Green Cities in Metropolitan Environments. Their environmentally friendly features and energy-efficient design complement larger metropolitan programs to lessen environmental footprints and build more resilient, sustainable urban ecosystems.
Positive Impact on Health and Well-Being:
Living spaces become healthier when eco-friendly materials, better air quality, and well-thought-out design components are prioritized. By reducing exposure to dangerous contaminants and promoting a sense of connection to nature, smart green houses seek to improve the general well-being of their occupants.
Promotion of Sustainable Practices:
Living in smart green houses encourages residents to adopt sustainable practices in their daily lives. This can include waste reduction, energy conservation habits, and a heightened awareness of environmental impact, contributing to a broader culture of sustainability.
Challenges and considerations of smart green houses:
While smart green houses offer a plethora of benefits, it’s essential to acknowledge and address certain challenges and considerations associated with their implementation. Here are key factors to be mindful of:
Initial Cost and Affordability:
Installing eco-friendly materials, renewable energy systems, and smart technology might come with a hefty upfront cost. Even though there will be substantial long-term energy bill savings, some homeowners may find the initial outlay difficult to make.
Technological Complexity:
Complexity might arise when integrating advanced technology like automation systems and Internet of Things devices. Problems with software upgrades, system compatibility, and the requirement for expert technical help might arise for homeowners.
Security Concerns:
Smart green houses are vulnerable to cybersecurity threats. As these homes become more interconnected, ensuring the security of personal data, automation systems, and IoT devices becomes paramount. Robust cybersecurity measures are necessary to safeguard against potential breaches.
Maintenance and repairs:
Although the goal of smart technologies is to minimize maintenance requirements, they also bring with them a new set of possible problems. Homeowners must be ready for the continuous upkeep of these technologies, since malfunctions in automated systems or sensors may call for professional technicians.
Limited Standardization:
Because there are no industry-wide protocols for smart homes, there are incompatibilities between various systems and gadgets. The smooth operation of smart green houses may be limited by the difficulties homeowners have when combining goods from different manufacturers.
Educational Barriers:
It’s possible that many homeowners are ignorant of the intricacies of sustainable practices and smart technology. To guarantee that homeowners can efficiently use and maintain the features of their smart green houses, closing the knowledge gap is essential.
Adaptation to Local Climates:
Certain environmentally friendly elements, including water management systems and renewable energy sources, may work differently in different climates. To get the most out of smart green houses, they need to be customized for certain environmental circumstances.
Regulatory and Zoning Challenges:
Zoning laws and construction requirements may not always be compatible with the cutting-edge characteristics of smart green houses. The implementation of sustainable construction principles may be slowed by the difficulties involved in navigating these regulatory environments.
Perception and aesthetics:
Some homeowners may resist the adoption of smart green features due to concerns about how these technologies may impact the aesthetic appeal of their homes. Balancing functionality with design is essential to addressing these aesthetic considerations.
Limited Availability of Skilled Professionals:
Smart green technology installation and upkeep may call for certain knowledge that is not generally accessible. In order for smart green houses to be widely used, it is imperative that workers be trained and developed to handle these sophisticated technologies.
Addressing these challenges through research, education, and continuous technological advancements is essential to realizing the full potential of smart green houses and ensuring their accessibility to a broader range of homeowners.
Conclusion:
Smart green houses represent a revolutionary approach to sustainable living, blending state-of-the-art technology with eco-conscious design. As the world continues to prioritize environmental stewardship, these homes offer a glimpse into a future where our dwellings actively contribute to a greener and more sustainable planet. Embracing the concept of smart green houses not only benefits individual homeowners but also plays a crucial role in shaping a more sustainable and resilient global future.